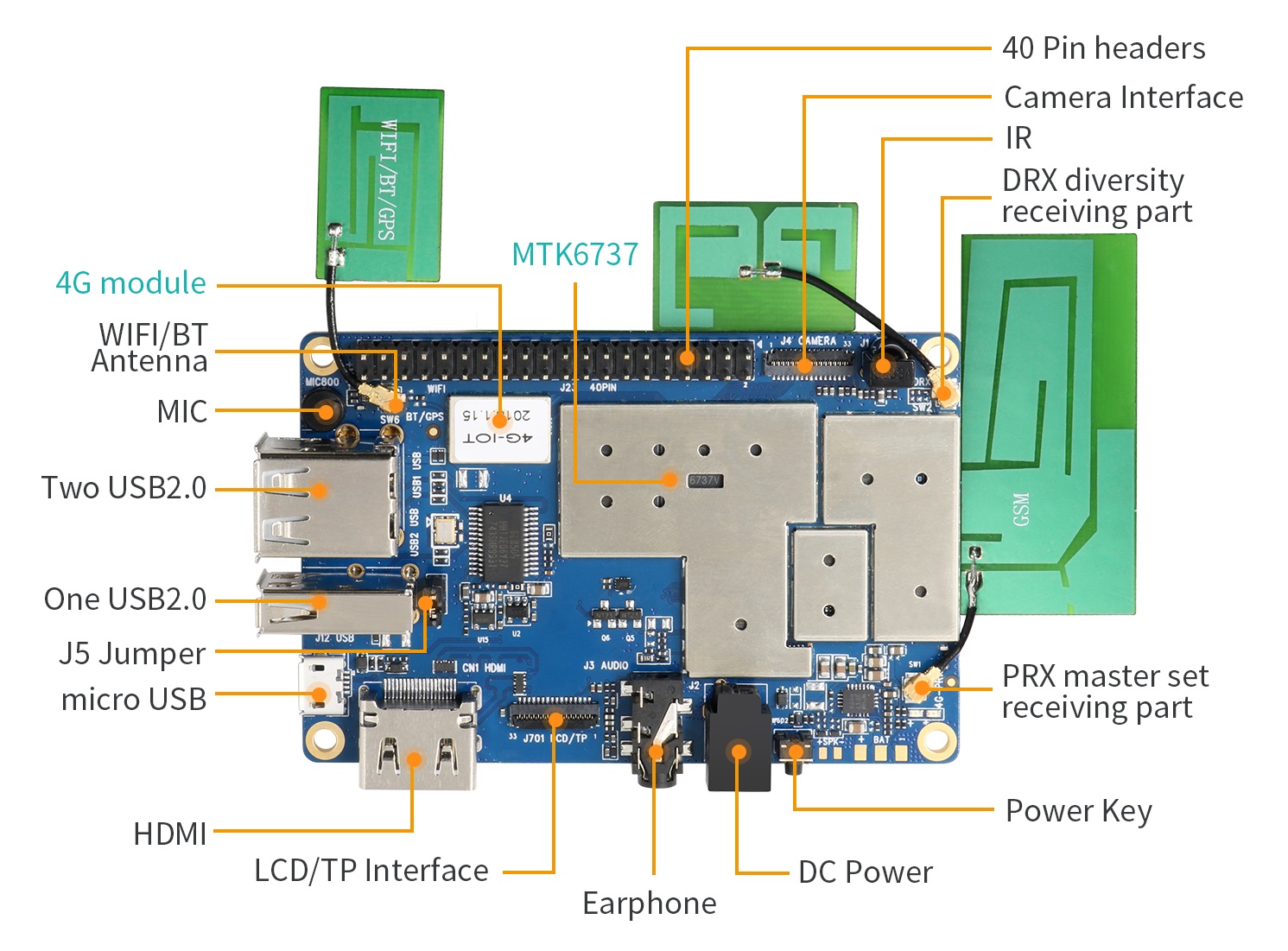
OrangePi 4G IoT. Source: orangepi.org
On the market came a new board for the Internet of things – OrangePi 4G IoT! In this review, we will take a closer look at the nuances of launching the board, software support and how much the board meets the expectations.
0. Short hardware review
With software support declared Android 6.0, Android Things is not supported. The working image of Linux at the time of writing the article did not exist. This, of course, limits and complicates the use of a board for connecting sensors with interfaces i2c, SPI, 1-Wire, etc.
Hardware specification | ||
| Processor | MT6737 | |
| CPU | Quad core ARM® Cortex-A53, Main frequency up to 1.25GHz | |
| GPU | • ARM Mali-T720 MP1 | |
| Memory | 1GB DDR3 | |
| Emmc | 8GB EMMC Flash | |
| Wireless | WIFI / BT / FM / GPS Four in one | |
| Radio frequency | GSM: 850/900/1800/1900 WCDMA: B1/B2/B4/B5/B8 TD-CDMA CDMA2000 FDD-LTE: B1/B2/B3/B4/B7/B17/B20 TDD-LTE: B38/40/41B | |
| Display | HD | |
| Capacitance touch | Support | |
| Camera | 13M (25pin ZIF Connector) | |
| Accelerometer Sensor | Support | |
| IR Control | Support (Adapted iDroid remote controller) | |
| Fingerprint Identification | Support | |
| SIM Card | mini Single SIM Card | |
| TF Card | Support hot-plugging | |
| Audio | Earphone: For audio input / output Mic: For audio input | |
| USB | USB Host × 3: Support OTG Micro USB × 1: Only for writing image | |
| LED | Power Indicator LED:Red Status Indicator LED: Green | |
| Key | Power | |
| HDMI | Support | |
| Low-level peripherals | 40pin Headers: 1.8V, SPI × 2 , I2C × 3, UART × 2 | |
| Power | DC : 5V 2A Battery:Connection through a weld plate | |
| OS | Android 6.0 | |
| Programming support | C、C++、Kotlin、Java、Shell、Pyhon | |
Interface definition | ||
| Size | 55mm × 85mm | |
| Weight | 43g | |
| Orange Pi is trademark of Shenzhen Xunlong Software CO., Limited | ||
Table 1. Official hardware specifications. Source: orangepi.org
The board slightly exceeded expectations:
| Type | Specifications | |
| Declared | Actual | |
| RAM | 1 GB | 2 GB |
| EMMC | 8 GB | 16 GB |
Table 2. Compare declared and real specifications
All other correspond to the declared. However, and so a good bonus 🙂
In comparison with other motherboards of this manufacturer, 4G IoT costs a lot – $ 45 (not including shipping costs), but it is well-founded.
| Type | Name | Wireless interfaces | Price |
| Modem | SIM808 | 2G | from 15 $ |
| Modem | SIM7100A | 4G/3G | from 10$ (just chip) to 43 $ (board) |
| Modem | Sierra Gobi5000 EM7355 | 4G/3G/2G | from 29$ |
| Modem | USB modems | 4G/3G/2G | от 20$ |
| Single board computer | OrangePi 4G IoT | 4G/3G/2G, WiFi, Bluetooth | 45 $ |
Table 3. Compare OrangePi 4G IoT with another modules
If we also take into account that when using an external module, add the same components to be equivalent to 4G IoT – we will exit almost at the same price + it is necessary to take into account the availability of software.
1. Run board and access to Android using Vysor
1.1 Short introduction
In the official documentation absent part of how to connect to board without display and keyboard. For example, for OrangePi 2G IoT you can use Vysor. But in the documentation for OrangePi 4G IoT micro USB port can be used only for, quote: Only for writing image. Sounds bad. But based on previous experience with specifications, I think, we have some easter eggs for this board.
And indeed it is! Onboard micro USB port has to modes – for firmware and for MTP Device. For change mode just remove J5. I got it experimentally way. Good bonus again 🙂
| J5 Status | Mode |
| Set | Firmware |
| Remove | MTP Device |
Table 4. Micro USB port modes
1.2 Install software
Install Mini ADB and Vysor (OS Windows).
1.3 Connect to board
By default, on the board must be installed Android 6.0. Check it – remove J5, connect 4G IoT to USB and press Power Button on five seconds. Wait, when to light up green led. In the system, a new device should appear MTP Device. If not, please wait 8-10 minutes, first run can be a long time.
If after 8-10 minutes board don’t start, then you must flash the firmware. You can see it in the official manual.
Attention! For flash firmware don’t forget set J5 on board!
1.4 Driver installation
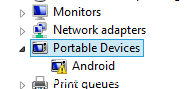
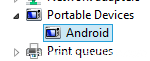
If device successfully running, in Control Panel a new device appears.
Wait when drivers installed or install manually. Right click on device Android and choose Update Driver Software.
Next, Browse my computer for driver software-> Let me pick from a list of device drivers on my computer->Choose MTP USB Device
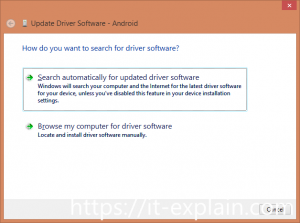
Picture 2. Choose driver
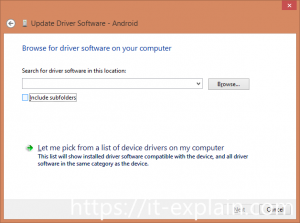
Picture 3. Choose driver
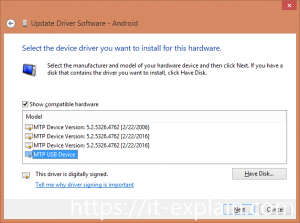
Picture 4. Choose driver
Picture 5. Choose driver
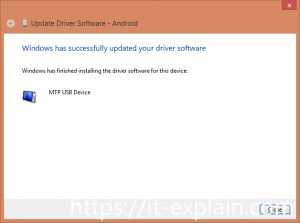
If driver successfully installed, you must see next in Control Panel:
Picture 6. Successfully driver installation
If OrangePi successfully started and driver successfully installed, run Vysor and connect.
1.5 Run Vysor and access to Android
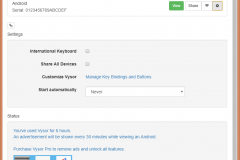
Run Vysor and check that device is visible. Then press View. Wait for connection and APK installation.
After this, you can connect to Android!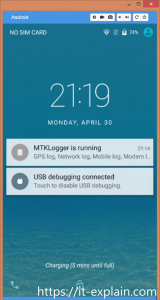
2. Review
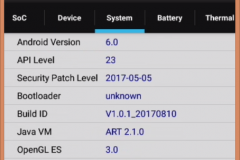
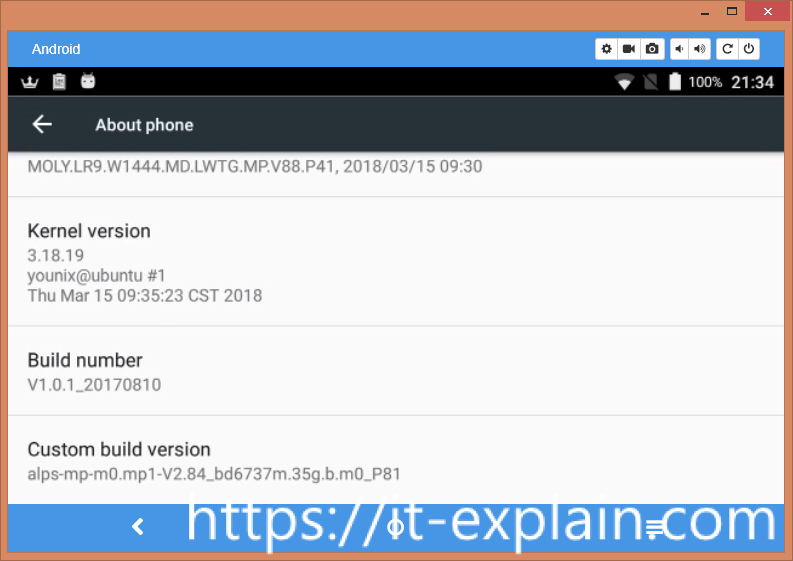
2.1 Kernel and Android
It’s an Android 6.0 with patches to 5 May 2017.
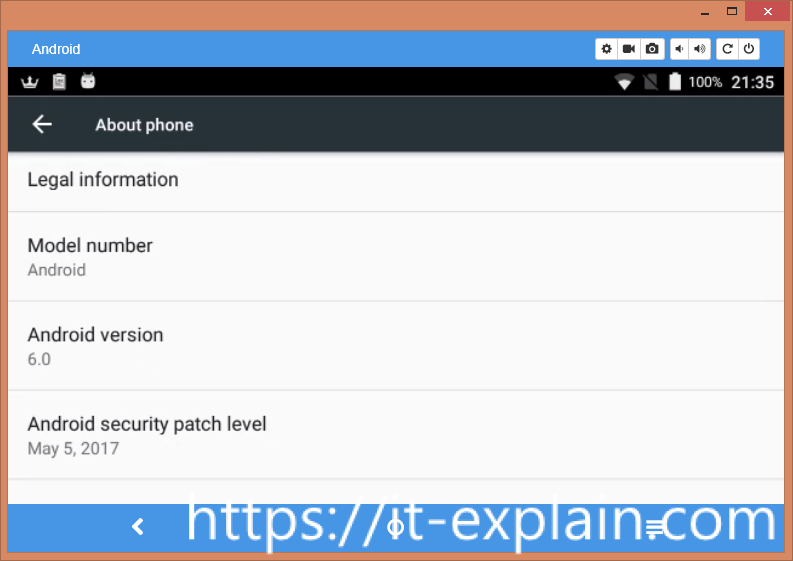
Kernel version is 3.18.19
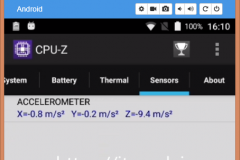
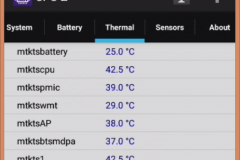
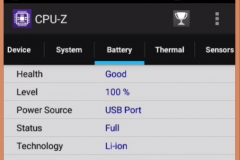
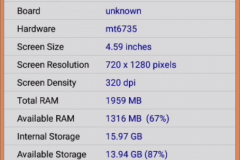
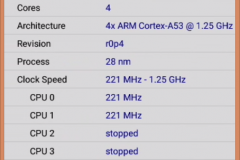
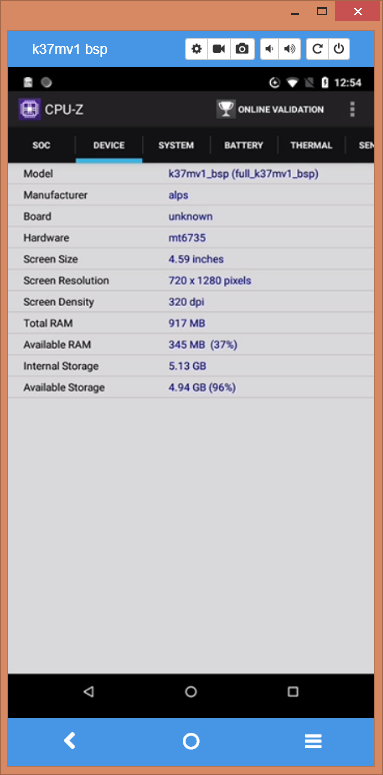
2.2 CPU, RAM, EMMC – CPU-Z
Added screenshots from CPU-Z. RAM – 2GB, EMMC – 16 GB! Not bad)
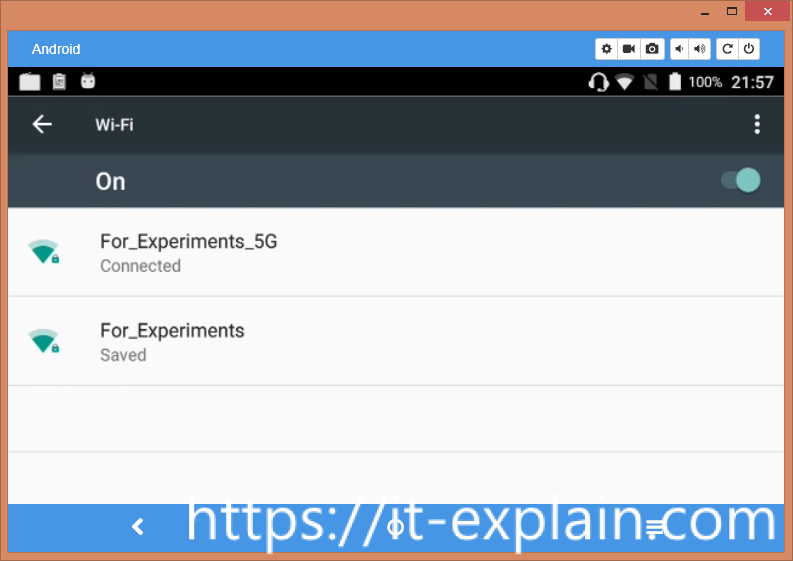
2.3 WiFi and 4G
I can’t test 4G now but tested WiFi interface. And WiFi on Orange Pi 4G IoT support 5GHz!
2.4 Additional functionality
OrangePi 4G IoT has microphone and IR sensor on board, but I couldn’t test it. But in Android, I found FM Radio application and it works. But don’t know any real case, wherein IoT need the radio 🙂
Also, the board has HDMI, but it realized using external chip LT8912B and haven’t a driver. In my test, I couldn’t connect my monitor to this board.
Capacitance touch sensor, Fingerprint Identification, Accelerometer Sensor, and GPS – very interesting points, but it necessary external components.
3. Conclusion
OrangePi 4G IoT has a very interesting hardware specification. Android support – good variant for development but for IoT it’s a not popular as a Linux. Android Things doesn’t support this single-board computer, so need to realize some functions for i2c, SPI, and GPIO on Android yourself or transfer from Android Things.
It’s a very interesting variant for IoT with support 4G/3G/2G networks and 5GHz WiFi. If you planning work with video/audio streams or in your country unavailable 2G networks or you Android developer, who want create something for IoT – OrangePi IoT 4G will be a good choice. But for simple meteorology stations or solutions which not require very speed internet or powerful CPU and RAM – it will be an expensive board. OrangePi have more another cheaper single-boards with Linux and Android support for this cases.
P.S. If you have questions or wishes – just write it in comments!
Updates after 28 July 2018.
After upgrade to Android 8.1 RAM – 1 GB, storage – 8 GB. Fantastic)
Updates after 10 October 2018
Try install Linux into chroot container using LinuxDeploy utility. It possible, but I can’t get stability root permissions. After reboot root permissions don’t work (for Android 8.1, for Android 6 is a problem get root permissions).
Tried Ubuntu and Debian. It works, but can’t access to i2c or direct to GPIO. No sense.
Looks like this board only for Android developers)
Updates after 30 December 2018
I tested Ubuntu Linux (installed into EMMC storage). It’s worked, but I don’t see modem device and can’t connect to GPS (using gpsd). Now I preparing an additional review for it. If you have any question or suggestions – please put these to comment after this article.